Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy | Gallbladder Surgery

Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy or minimally invasive gallbladder removal is a procedure performed to remove the gallbladder from the body. This is a keyhole surgery and therefore allows the surgeon to perform the surgery through small incisions in the abdomen. Narrow instruments called a laparoscope, with a camera at the tip of the scope, is inserted through the incisions. The doctor visualizes the internal structures through the scope on a video monitor and thus performs the surgery.
Gallbladder
The gallbladder is a small pear shaped organ that aids in the digestion process. The organ stores a fluid made by the liver called bile. Bile is a dark yellow fluid that helps digests fats in the gut. Gallbladder lies just beneath the liver and transports bile to the small intestine through narrow channels known as bile ducts.

Cholelithiasis / Gallbladder Stones
Gallstones or gallbladder stones is the most common cause of gallbladder disease. Gallstones are crystals that form inside the gallbladder. The gallbladder stone crystals are formed when too much cholesterol or too much bilirubin gets accumulated in the organ or in the duct. As a result, it prevents the flow of digestive enzymes.
Cholelithiasis is the term used to describe the condition of having gallstones. “Chole” means bile and “lithiasis” means forming of stones.
Gallstones that move out of the gallbladder can pass into the stomach. But sometimes the stone can become lodged in the bile duct due to the size of the stone. Thus, gallbladder stones that have become lodged in the bile duct are bile duct stones.
Presence of gallstones in the bladder or duct results in swelling, pain, indigestion and vomiting as they block the flow of enzymes through bile duct to the small intestine. If gallbladder stones or bile stones are left untreated, it can cause severe medical condition and leads to jaundice. Therefore, it is important to treat Cholelithiasis.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is the term used to describe inflammation of the gallbladder. In most cases, gallstones is the main cause for cholecystitis. It is important to treat cholecystitis as it can lead to severe and life-threatening complications such as rupture of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy or gallbladder removal is performed in such cases.
Diagnosing Cholelithiasis / Gallstones
Ultrasound scanning is used to diagnose gallstones. Nuclear Medicine Scans are performed for complex cases.
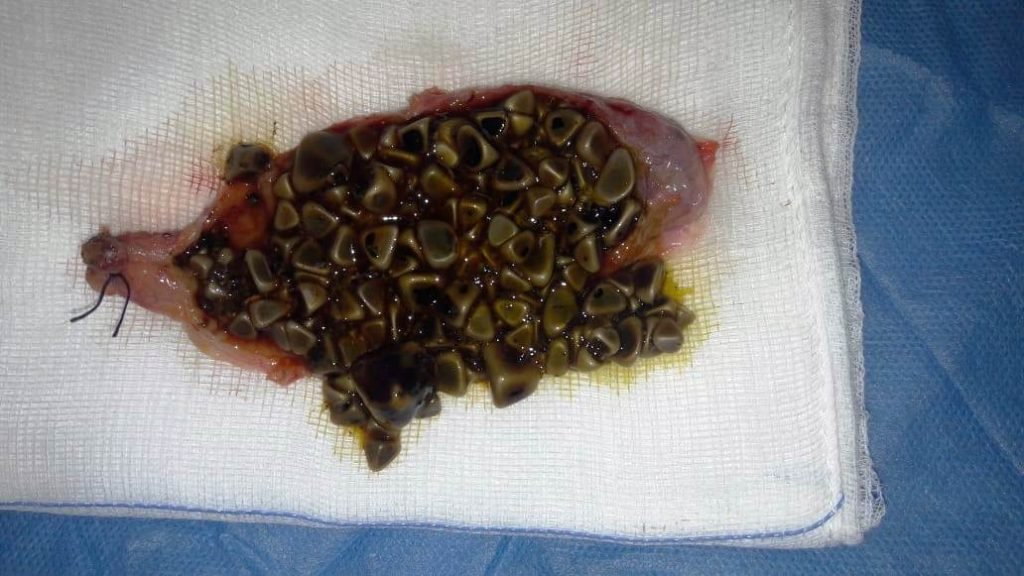
Picture showing Gallbladder stones
Treatment for gallbladder disorders
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the most commonly used treatment method for removal of gallbladder along with gallstones. Laparoscopic Surgeries are also known as Minimally Invasive Surgeries (MIS) as it uses keyhole incisions. The surgeon initiates the procedure by administering general anesthesia and the patient is put to sleep. Once anesthesia is achieved, the surgeon makes an incision in the navel area of the abdomen. The surgeon inserts a cannula through which a laparoscope is inserted.

A laparoscope is an instrument that has a telescope attached to a video camera. This helps to capture enlarged images of the organs enabling the surgeon to view in detail the condition of the organ and the surrounding internal cavity.
After inspection of the organ, few more incisions are made to insert specially designed instruments and other surgical tools to remove the bladder. During the operation cholangiogram may be performed to identify stones that could be lodged in the bile ducts. If gallstones are detected in the ducts, they are also removed.
The incisions are then closed by surgical clips or stitches. The surgery generally last for one or two hours.
Most patients can leave the hospital on the same day itself. However, proper care should be taken with proper medications and self care. If any symptoms like fever, pain in the abdomen area, frequent vomiting, or pus discharge from the incisions are noticed, immediately consult the doctor. Patients can engage in day to day activities within a week.
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy vs. Open Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimal invasive procedure with faster recovery and less pain. As a result, most patients can be discharged same day itself. After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, patients experience lesser postoperative pain when compared to open surgery and have a fast recovery. Therefore, laparoscopy is preferred to open surgery.
About Dr. R. Padmakumar
Dr. R. Padmakumar is one of the Best Hernia Surgeon in India. He has been changing lives through Keyhole Surgery. He has got more than 30 years of hands-on experience in laparoscopic Surgery in major hospitals across India and has completed more than 7000 cases of Laparoscopic Hernia Surgeries. Dr. Padmakumar has trained more than 300 surgeons from all over the world the art of laparoscopic surgery especially Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery. Dr. Padmakumar is also hailed as one of the Best Bariatric Surgeon in India & UAE. He is renowned for new and improved treatment techniques and the first in the World to perform Scarless Bariatric Surgery with Tummy Tuck / Abdominoplasty. He is also one of the very few thyroid surgeons in India doing Endoscopic Thyroidectomy (scarless thyroid surgery).


-
Anal Fissure Treatment
-
Gynaecomastia Treatment
- Piles / Hemorrhoids Treatment
- Varicose Veins Treatment
- Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins
- Diabetic Foot Treatment